Self-Lubricating Joint Bearings Cut Maintenance Costs by 70%: The Future of Industrial Efficiency
In today's fast-paced industrial landscape, reducing downtime and maintenance costs is a top priority. Self-lubricating joint bearings or rod end ball joint have emerged as a game-changing solution, offering up to 70% lower maintenance costs compared to traditional bearings. These innovative rod end ball joint or female rod end bearing are transforming industries from automotive manufacturing to renewable energy, delivering unmatched reliability and efficiency.
How Self-Lubricating joint bearings or rod end ball joint Work
Unlike conventional bearings that require regular greasing, self-lubricating joint bearings integrate solid lubricants (such as PTFE, graphite, or MoS₂) into their sliding layers. This design of joint bearings ensure:
✔ Continuous lubrication – No need for manual re-greasing
✔ Reduced friction – Coefficient as low as 0.05–0.10
✔ Longer service life – Up to 3–5x longer than standard bearings
✔ Contamination resistance – Ideal for dirty or wet environments
Industries Benefiting the Most
1. Heavy Machinery & Construction
Excavators, cranes, and mining equipment experience 40% less wear with self-lubricating joint bearings (rod end ball joint and female rod end bearing ).
Case Study: A German mining company use self-lubricating joint bearings (rod end ball joint and female rod end bearing ), such as 1 4 20 female rod end, 5 16 rod end ball joint, which reduced bearing replacements from quarterly to once every 2 years.
2. Automotive & Robotics
Self-lubricating joint bearings (rod end ball joint and female rod end bearing ) Used in suspension systems, steering linkages, and robotic arms.
Tesla’s Gigafactories report 30% fewer maintenance stops after switching to self-lubricating bearings, such as 1 4 20 female rod end, 5 16 rod end ball joint.
3. Marine & Offshore Applications
Saltwater corrosion? No problem. These bearings withstand harsh marine conditions without degradation.
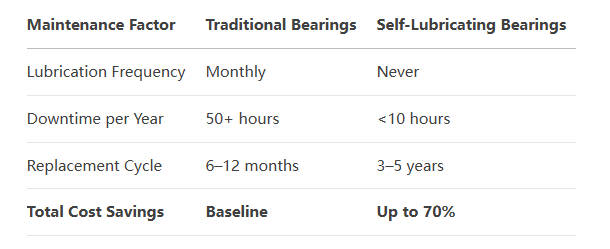
Cost Savings Breakdown
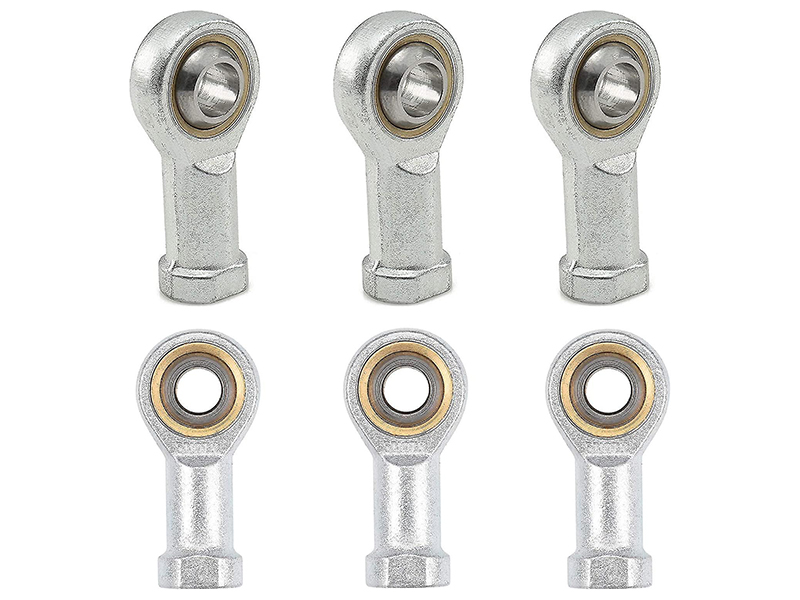
female rod end bearing : 1 4 20 female rod end
Key Specifications of 1 4 20 female rod end:
Thread: 1/4"-20 UNF (Unified Fine Thread, 20 TPI)
Gender: Female (internal threads)
Type: Spherical plain bearing / rolling element
Load Capacity of 1 4 20 female rod end:
Dynamic Radial: ~500 kg
Dynamic Axial: ~200 kg
Materials of 1 4 20 female rod end:
Body: Carbon steel (zinc-plated) / Stainless steel (304/316)
Ball: Chrome steel (HRC 58-62)
Sealing: Rubber seals or PTFE-lined (maintenance-free option)
Typical Applications
Precision mechanisms: 3D printer linkages, RC vehicle steering
Industrial automation: Conveyor belt adjusters, sensor mounts
Automotive: Throttle linkages, suspension tuning
Advantages
✔ Fine adjustment: 0.05mm-level precision with UNF threads
✔ Compact: Total length typically <40mm
✔ Corrosion-resistant: 316SS version for harsh environments
joint bearings : 5 16 rod end ball joint
Key Specifications of 5 16 rod end ball joint:
Thread: 5/16"-24 UNF (or 5/16"-18 UNC)
Gender: Male (external threads) standard (female available)
Design: Ball-and-socket joint (±25° articulation)
Load Capacity of 5 16 rod end ball joint:
Dynamic Radial: ~800 kg
Dynamic Axial: ~350 kg
Materials of 5 16 rod end ball joint:
Ball: Alloy steel (hardened & ground)
Housing: Forged steel / Aerospace aluminum (lightweight)
Temperature: -30°C to +120°C (high-temp versions to 250°C)
Typical Applications
Heavy equipment: Tractor suspension, hydraulic cylinders
Aerospace: Flight control linkages (MIL-SPEC compliant)
Motorsports: Shift mechanisms, push-rod suspensions
Advantages of female rod end bearing
✔ High rigidity: Forged housing withstands 50% more shock loads
✔ Misalignment compensation: Tolerates ±3° shaft deflection
✔ Modular: Replaceable ball head without full disassembly
















